An Exploration of Diaphragm, Glottis, and Pelvic Floor Connection
An Exploration of Diaphragm, Glottis, and Pelvic Floor Connection
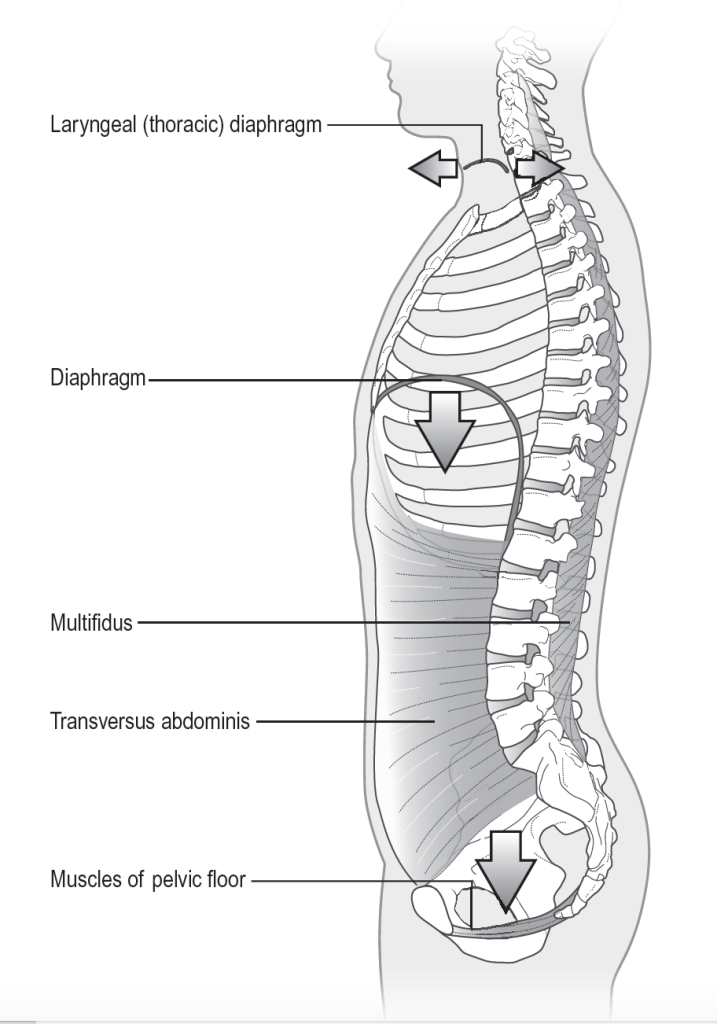
Breathing is a fundamental process that sustains life, but its significance extends beyond mere respiration. In the realm of pelvic physiotherapy, breathing techniques play a vital role in optimizing pelvic floor function and promoting overall pelvic health. This article delves into the intricate connection between the diaphragm, glottis, and pelvic floor, elucidating the anatomy of these structures and highlighting how breathing techniques can be utilized to enhance pelvic physiotherapy outcomes.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Diaphragm, Glottis, and Pelvic Floor
- The Diaphragm: The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located beneath the lungs, separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. It serves as the primary muscle responsible for breathing. When it contracts, it flattens and descends, creating negative pressure in the chest cavity and allowing the lungs to expand with air. The diaphragm attaches to the lower ribcage, the sternum, and the spine, forming a muscular barrier at the base of the thoracic cavity.
- The Glottis: The glottis refers to the opening between the vocal cords in the larynx, which controls airflow during breathing, swallowing, and speaking. It consists of the vocal folds, which are elastic bands of tissue that vibrate to produce sound. The glottis opens during inhalation to allow air to enter the respiratory system and closes during swallowing to prevent food or liquid from entering the airway.
- The Pelvic Floor: The pelvic floor refers to a group of muscles, ligaments, and connective tissues that span the bottom of the pelvis. It acts as a hammock-shaped structure, providing support to the pelvic organs, including the bladder, uterus, and rectum. The pelvic floor muscles play a crucial role in urinary and fecal continence, sexual function, and stabilizing the pelvic region. These muscles can be divided into three layers: superficial, middle, and deep, each with specific functions and connections to other anatomical structures.
The Connection between Breathing and the Pelvic Floor
Breathing and the pelvic floor are intricately connected through the coordination of the diaphragm, glottis, and pelvic floor muscles. When you inhale, the diaphragm contracts and descends, causing the abdominal contents to be pushed downward and the pelvic floor to relax. This coordination creates an optimal environment for efficient diaphragmatic breathing and proper pelvic floor function.
The Importance of Diaphragmatic Breathing
Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing or deep breathing, refers to the practice of engaging the diaphragm fully during the inhalation and exhalation process. This technique is crucial in pelvic physiotherapy for several reasons:
- Pelvic Floor Activation: Diaphragmatic breathing promotes the engagement and coordination of the pelvic floor muscles. As the diaphragm descends during inhalation, the pelvic floor muscles naturally relax, allowing for optimal expansion of the abdominal cavity. On exhalation, the diaphragm ascends, and the pelvic floor muscles contract, providing support to the pelvic organs.
- Improved Diaphragm Mobility: Deep breathing exercises help improve the mobility and excursion of the diaphragm. This enhanced mobility allows for better ventilation and oxygenation of the lungs, reducing respiratory inefficiencies and promoting overall lung health.
- Stress and Tension Reduction: Diaphragmatic breathing activates the body's relaxation response, promoting a sense of calm and reducing stress levels. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with pelvic floor dysfunction, as stress and tension can contribute to pelvic pain, muscle tightness, and other pelvic floor disorders. By incorporating diaphragmatic breathing into pelvic physiotherapy, individuals can effectively manage stress and alleviate tension in the pelvic region.
Techniques for Incorporating Diaphragmatic Breathing in Pelvic Physiotherapy
- Mindful Breathing: Begin by finding a comfortable position, either sitting or lying down. Place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen. Take slow, deep breaths, focusing on filling your abdomen with air as you inhale. Feel your abdomen rise and fall with each breath. This technique promotes diaphragmatic engagement and relaxation of the pelvic floor.
- Breathing with Pelvic Floor Muscle Activation: Combine diaphragmatic breathing with pelvic floor muscle activation to enhance coordination. As you inhale, relax your pelvic floor muscles, allowing them to naturally descend with the diaphragm. On exhalation, gently contract the pelvic floor muscles, lifting them back up. This synchronized movement strengthens the connection between the diaphragm and the pelvic floor.
- Yoga and Pilates-Based Breathing Exercises: Yoga and Pilates incorporate various breathing techniques that can be beneficial for pelvic health. Techniques such as "Ujjayi" breath or "Pilates Breathing" emphasize deep, controlled breathing, engaging the diaphragm and promoting relaxation and coordination with the pelvic floor muscles.
- Integrated Breathing during Exercises: During pelvic floor exercises or other therapeutic movements, it is essential to maintain proper breathing. Coordinate your breath with the movements, ensuring that inhalation aligns with relaxation and lengthening of the pelvic floor, while exhalation corresponds with contraction and engagement of the pelvic floor.
Benefits of Incorporating Breathing Techniques in Pelvic Physiotherapy
- Enhanced Pelvic Floor Function: By incorporating diaphragmatic breathing, individuals can optimize the coordination between the diaphragm and the pelvic floor, improving muscle tone, relaxation, and overall function.
- Stress and Pain Reduction: Diaphragmatic breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing stress levels and promoting relaxation. This can help alleviate pelvic pain, muscle tension, and other symptoms associated with pelvic floor dysfunction.
- Mind-Body Connection: Breathing techniques foster a deeper mind-body connection, allowing individuals to be more in tune with their pelvic floor muscles and body sensations. This increased awareness can lead to better control, coordination, and self-management of pelvic health.
Incorporating Breathing Techniques into Daily Life
Apart from incorporating breathing techniques during specific pelvic physiotherapy sessions, it is beneficial to integrate them into daily life. Practicing diaphragmatic breathing during activities such as sitting, standing, or exercising can support pelvic floor health and overall well-being. Mindful breathing exercises, relaxation techniques, and stress management practices can be valuable tools for maintaining pelvic health beyond formal therapy sessions.
Breathing techniques, particularly diaphragmatic breathing, play a crucial role in pelvic physiotherapy by optimizing the coordination between the diaphragm, glottis, and pelvic floor muscles. By engaging in deep breathing exercises, individuals can enhance pelvic floor function, promote relaxation, improve circulation, and reduce stress levels. Incorporating breathing techniques into pelvic physiotherapy interventions and daily life can lead to better pelvic health, improved overall well-being, and a stronger mind-body connection. Embrace the power of your breath and unlock the potential for optimal pelvic health.


