Find out what the differences are.
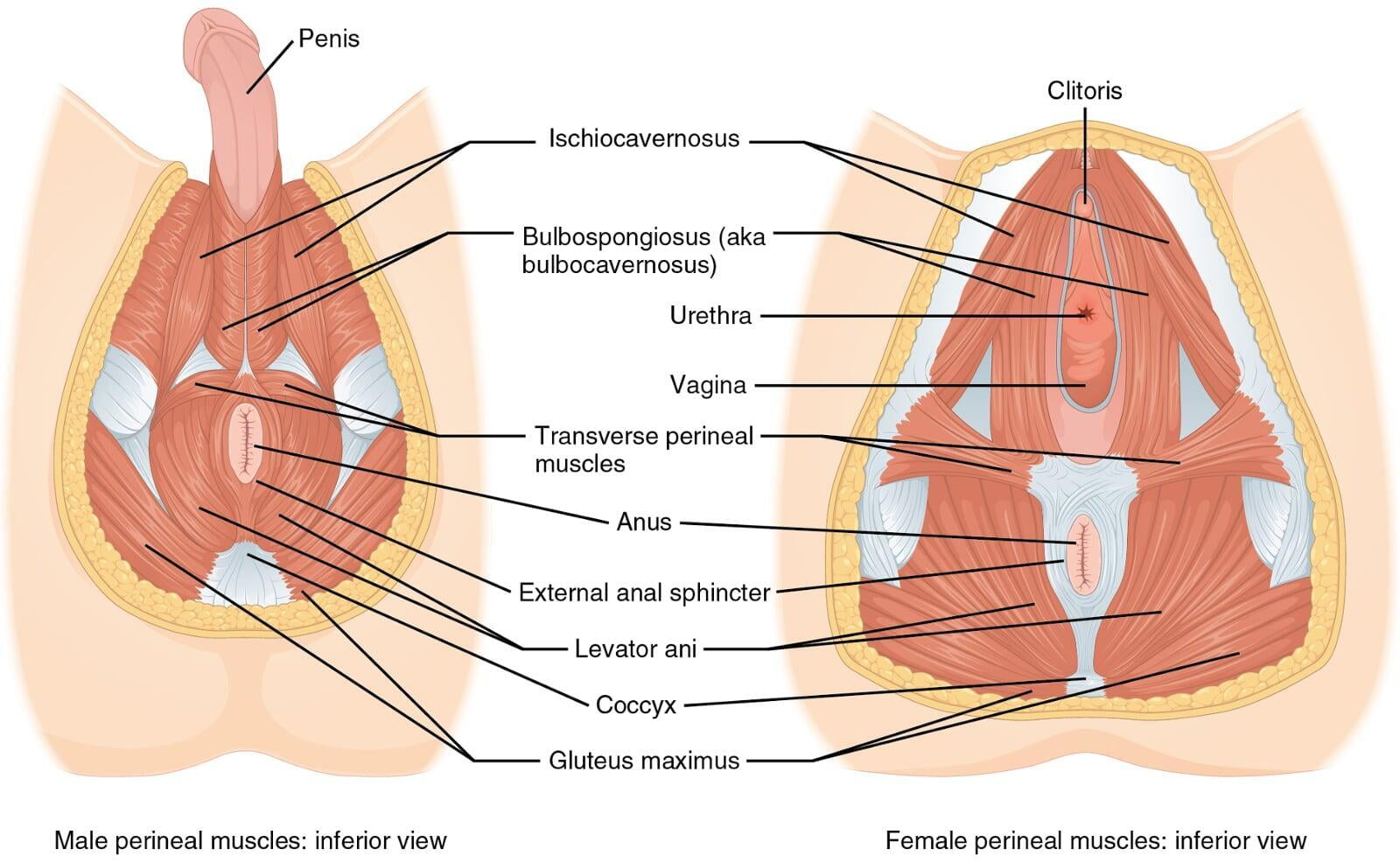
The pelvic floor is a group of muscles and connective tissues that support the pelvic organs, including the bladder, rectum, and uterus (in females). Both men and women have a pelvic floor, but there are some differences between the male and female pelvic floor. In this article, we will explore the anatomy and function of the male and female pelvic floor and their differences.
Anatomy of the Pelvic Floor:
The pelvic floor is a group of muscles that form a hammock-like structure at the bottom of the pelvis. These muscles are arranged in layers and attach to the pubic bone, coccyx (tailbone), and the walls of the pelvis. The pelvic floor muscles can be divided into three main layers:
The superficial layer: This layer consists of the bulbo-spongiosus and ischiocavernosus muscles in males and the bulbocavernosus, ischiocavernosus, and transverse perineal muscles in females.
The middle layer: This layer consists of the urogenital diaphragm in both males and females, and it supports the urethra and vagina.
The deep layer: This layer consists of the levator ani muscles in both males and females, and it provides support for the pelvic organs.
Differences between the Male and Female Pelvic Floor:
While the anatomy of the pelvic floor is similar in both males and females, there are some differences in their structure and function.
- The Urogenital Diaphragm:
The urogenital diaphragm is a muscular sheet that supports the urethra and vagina in females and the urethra and prostate gland in males. In females, the urogenital diaphragm is thicker and stronger than in males due to the need to support the weight of the uterus and the baby during pregnancy.
- The Pubococcygeus (PC) Muscle:
The PC muscle is a major component of the pelvic floor, and it is responsible for maintaining continence and sexual function. In females, the PC muscle surrounds the vagina and the anus, while in males, it surrounds the anus and the base of the penis. The PC muscle is stronger in females than in males, which is believed to be due to the need for childbirth.
- Pelvic Organ Prolapse:
Pelvic organ prolapse is a condition where the pelvic organs descend or protrude into the vaginal canal due to weakened pelvic floor muscles. This condition is more common in females than in males because the female pelvic floor supports the weight of the uterus and the baby during pregnancy and childbirth.
- Urinary Incontinence:
Urinary incontinence is a common condition where a person loses control of their bladder and leaks urine. It is more common in females than in males because the female urethra is shorter than the male urethra, and the female pelvic floor is more prone to weakness due to pregnancy and childbirth. However, post-prostatectomy surgery, males may experience considerable amount of urine loss.
- Prostate Issues:
The prostate gland is a male reproductive organ that is located just below the bladder. As men age, the prostate gland may become enlarged and cause urinary symptoms. The prostate gland is not present in females, and they do not experience the same issues related to prostate health.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, while the male and female pelvic floor have some similarities, there are also some differences in their anatomy and function. The female pelvic floor is generally stronger and thicker than the male pelvic floor due to the need to support the weight of the uterus and the baby during pregnancy and childbirth. Additionally, females are more prone to pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence than males due to their unique anatomy and physiology. Understanding the differences between the male and female pelvic floor can help healthcare professionals provide better care and treatment for patients.


